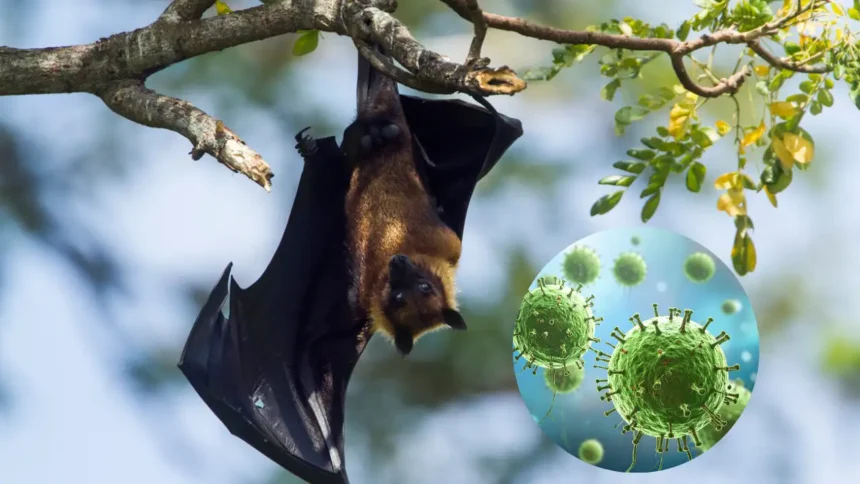
Health authorities in India are currently dealing with a serious outbreak of Nipah virus that has raised concerns across the country and beyond. With five confirmed cases in West Bengal and nearly 100 people placed under quarantine, the deadly Nipah virus has once again proven why it remains one of the most dangerous health threats we face today.
In this detailed guide, we will help you understand what Nipah virus is, how it spreads, what symptoms to watch for, and most importantly, how you can protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially fatal infection.
What Is Nipah Virus and Why Should You Care

Nipah virus is a dangerous virus that spreads from animals to humans. Scientists first discovered this virus in 1998 during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore. The virus gets its name from Sungai Nipah, a small village in Malaysia where doctors first identified it.
What makes Nipah virus extremely concerning is its high death rate. Studies show that between 40 and 75 out of every 100 people infected with this virus may die. This makes it more deadly than many other viral infections, though thankfully it does not spread as easily as diseases like COVID-19.
The virus belongs to a group called Henipavirus and can cause serious breathing problems and swelling in the brain. The World Health Organization has listed Nipah virus as a priority disease because of its potential to cause widespread outbreaks and the fact that we currently have no approved vaccine or specific treatment for it.
Current Nipah Virus Outbreak in India 2026
The latest Nipah virus outbreak began in January 2026 when two nurses working at Narayana Multispeciality Hospital in Barasat, near Kolkata, fell sick with high fever and breathing difficulties. They developed symptoms between December 28 and December 30, 2025, and were admitted to intensive care on January 4, 2026.
Health officials confirmed these as Nipah virus cases on January 13, 2026, after testing at the National Institute of Virology in Pune. Since then, three more healthcare workers have tested positive, including a doctor, another nurse, and a health staff member. This brings the total confirmed cases to five.
The government has taken quick action by placing nearly 100 people who came in contact with infected patients under home quarantine for 21 days. One of the infected nurses remains in critical condition, while the male nurse is showing signs of improvement. Several states across India have been put on high alert to prevent the virus from spreading further.
How Does Nipah Virus Spread
Transmission from Animals to Humans
Fruit bats, also called flying foxes, are the natural carriers of Nipah virus. These bats belong to the Pteropus family and can carry the virus without getting sick themselves. Humans can become infected in several ways.
The most common way people get infected is by eating fruits or drinking liquids that have been contaminated with bat saliva, urine, or droppings. In some countries like Bangladesh, people who drink raw date palm sap are at higher risk because bats often feed on these trees at night and leave behind infected fluids.
Contact with sick animals like pigs can also spread the virus. During the first outbreak in Malaysia, most people got infected after close contact with sick pigs or their body fluids.
Person to Person Transmission
Unlike the first outbreak, recent Nipah virus cases have shown that the virus can spread from one person to another. This happens through close contact with body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, or respiratory droplets from an infected person.
Healthcare workers and family members who care for sick patients face the highest risk. This is exactly what happened in the current West Bengal outbreak, where hospital staff became infected while treating patients.
Nipah Virus Symptoms You Need to Know
Early Warning Signs
The time between exposure to the virus and showing symptoms usually ranges from 4 to 14 days, though in rare cases it can take up to 45 days. Early symptoms of Nipah virus infection look very similar to common flu, which is why many cases go unnoticed at first.
People infected with Nipah virus typically experience fever, headache, muscle pain, vomiting, and sore throat in the beginning. Some may also develop a cough and difficulty breathing. These initial symptoms can last for 3 to 14 days.
Severe Symptoms and Complications
As the infection progresses, things can become serious very quickly. The virus can attack the brain, causing a condition called encephalitis or brain swelling. When this happens, patients may feel dizzy, extremely drowsy, confused, or disoriented.
In severe cases, people may experience seizures and slip into a coma within just 24 to 48 hours. Some patients develop acute respiratory distress, where their lungs stop working properly and they need ventilator support to breathe.
Even those who survive may not fully recover. About 20 out of every 100 survivors experience long-term problems like recurring seizures, personality changes, or other brain-related issues. In some rare cases, people who seemed to recover have fallen sick again months or even years later.
Stay Informed About Health Updates: For more information on health concerns affecting men and their families, visit Mensbuddy.com where we share reliable health tips and the latest medical news in simple language.
Who Is at Risk of Getting Nipah Virus
Not everyone faces the same level of risk when it comes to Nipah virus infection. Understanding who is most vulnerable can help you take the right precautions.
Healthcare workers stand at the frontline of risk. Doctors, nurses, and hospital staff who treat infected patients without proper protective equipment can easily catch the virus. This is why five healthcare workers got infected in the recent West Bengal outbreak.
People living in or traveling to areas where outbreaks occur should be extra careful. Countries like Bangladesh and India have seen repeated outbreaks, especially in states like Kerala and now West Bengal. If you live near forests or areas where fruit bats are common, your risk is higher.
Those who work with animals, particularly pig farmers, also face increased risk. Family members and caregivers of sick patients need to be extremely cautious as the virus spreads through close contact.
Nipah Virus Prevention Tips Everyone Should Follow
Basic Safety Measures
Since there is no vaccine available yet, prevention is your best defense against Nipah virus. The good news is that following some simple steps can significantly reduce your risk of infection.
Always wash your hands properly with soap and water, especially before eating or after touching animals. This simple habit can protect you from many infections, including Nipah virus.
Be very careful about the fruits you eat. Avoid eating fruits that show signs of bat bites or that have been partially eaten. Always wash fruits thoroughly under running water and peel them before eating. Some experts recommend avoiding eating fruits that grow in areas where bats are commonly seen.
Never drink raw date palm sap or other fresh juices sold in open containers, especially in areas where Nipah outbreaks have occurred. If you must consume such products, make sure they are boiled first.
Protecting Yourself from Sick People and Animals
Stay away from people who show symptoms of Nipah virus infection, such as high fever with confusion or breathing difficulties. If you must care for a sick family member, use proper protective equipment like masks and gloves, and avoid direct contact with their body fluids.
Do not touch sick or dead animals, especially bats and pigs. If you work with animals, use protective clothing and wash yourself thoroughly after work.
If you live in an area with fruit bat populations, avoid places where bats gather or roost. Do not enter bat caves or disturb bat colonies.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Nipah Virus
How Doctors Diagnose Nipah Virus
Diagnosing Nipah virus can be challenging because early symptoms look like many other common illnesses. Doctors become suspicious when someone develops fever and brain-related symptoms in an area where Nipah cases have been reported.
During the early stage of infection, doctors use a test called RT-PCR that can detect the virus in throat swabs, blood, urine, or spinal fluid. Later in the infection or after recovery, blood tests can find antibodies that show whether someone had the virus.
Available Treatment Options
Unfortunately, we do not have any approved medicine that can specifically kill the Nipah virus. This makes prevention even more important. When someone gets infected, doctors focus on supportive care to help the body fight the infection.
Supportive care includes giving plenty of fluids, managing fever and other symptoms, and providing breathing support with ventilators when needed. Patients with severe symptoms need intensive care in isolation rooms to prevent spreading the virus to others.
Scientists are working hard to develop treatments. Some experimental medicines like monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs such as Remdesivir have shown promise in animal studies, but they are not yet approved for regular use. Several vaccine candidates are also in various stages of testing, with a vaccine called ChAdOx1 NipahB currently in clinical trials.
History of Nipah Virus Outbreaks

Learning about past outbreaks helps us understand how serious this virus can be. The first recognized outbreak happened in 1998-1999 in Malaysia and Singapore. During this outbreak, 276 people got infected, mostly pig farmers, and 106 people died. The Malaysian government had to kill more than one million pigs to control the outbreak.
Since then, India and Bangladesh have faced regular outbreaks. Kerala state in India has experienced multiple outbreaks since 2018, with the deadliest one that year killing 17 out of 18 infected people. Bangladesh has reported cases almost every year since 2001, with a total of 343 cases and 245 deaths by 2024.
The virus found in Bangladesh and India appears to be slightly different from the Malaysian strain. The South Asian strain spreads more easily from person to person, making it potentially more dangerous.
What Makes Nipah Virus So Dangerous
Several factors make Nipah virus particularly scary for health experts. First, the death rate is extremely high compared to most other viral diseases. While COVID-19 has a death rate of about 2 percent, Nipah can kill 40 to 75 percent of infected people.
Second, the virus can attack multiple organs in the body. It causes problems in the lungs, making it hard to breathe, and in the brain, causing swelling and seizures. This double attack makes treatment very difficult.
Third, we have no vaccine or specific medicine to prevent or treat it. This means we can only rely on supportive care, which is not always enough for severely sick patients.
Fourth, the virus can spread through multiple routes including contaminated food, sick animals, and infected people. This makes it harder to control outbreaks.
Finally, fruit bats that carry the virus are found across many tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa, and the Pacific. This means the potential for outbreaks exists in many countries where these bats live.
What Governments and Health Agencies Are Doing
Indian health authorities have responded quickly to the current outbreak. They have set up isolation wards in hospitals, placed contacts under quarantine, and issued alerts to all states to watch for any suspected cases.
The government has deployed special teams to trace everyone who came in contact with infected patients. Testing facilities have been activated across several states to ensure quick diagnosis of any new cases.
The World Health Organization is closely monitoring the situation and providing technical support to affected countries. They have emphasized the need for better surveillance systems to detect cases early and prevent spread.
Research organizations worldwide are working on developing vaccines and treatments. Several promising candidates are in different stages of testing, offering hope that we may soon have effective tools to fight this deadly virus.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nipah Virus
Can Nipah virus spread through air like COVID-19?
No, Nipah virus does not spread through air over long distances like COVID-19. It spreads mainly through close contact with infected people or animals, or by consuming contaminated food and drinks. However, it can spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes nearby, so maintaining distance from sick people is important.
Is there any vaccine available for Nipah virus?
Currently, there is no approved vaccine for Nipah virus available to the public. However, several vaccine candidates are being tested in clinical trials, including one called ChAdOx1 NipahB that started Phase 1 trials in 2024. Scientists are working hard to develop an effective vaccine as quickly as possible.
Can you get Nipah virus twice?
Most people who recover from Nipah virus develop antibodies that should protect them from getting infected again. However, in rare cases, some people have experienced symptoms months or years after their initial recovery, suggesting the virus may remain dormant in the body. More research is needed to fully understand immunity after infection.
How long should someone stay in isolation if infected with Nipah virus?
Infected patients should remain isolated until they test negative for the virus and show no symptoms. This typically means staying in isolation until doctors confirm complete recovery through laboratory tests. Close contacts of infected people should quarantine themselves for 21 days and watch for any symptoms.
Are children more at risk than adults?
Nipah virus can affect people of all ages. However, the risk depends more on exposure than on age. Healthcare workers, caregivers, and people living in outbreak areas face higher risk regardless of their age. Children may be more vulnerable to severe complications if they get infected, so extra care should be taken to keep them away from affected areas.
What should I do if I think I have Nipah virus symptoms?
If you develop symptoms like high fever, headache, confusion, or breathing difficulty, especially if you live in or recently visited an area where Nipah cases have been reported, seek medical help immediately. Call ahead to inform the hospital about your symptoms so they can take proper precautions. Do not wait for symptoms to get worse, as early medical care improves chances of survival.
Can eating properly cooked food protect me from Nipah virus?
Yes, cooking food thoroughly can kill the Nipah virus. If you must consume products that could be contaminated by bats, such as date palm sap, boiling them properly makes them safe. Always wash and peel fruits before eating them. Avoid eating any fruits that show bite marks or appear to have been partially eaten by animals.
Is it safe to travel to areas where Nipah outbreaks occur?
While it is not completely unsafe to travel to these areas, you should take extra precautions. Avoid visiting hospitals treating Nipah patients unless absolutely necessary. Follow all food safety guidelines, practice good hand hygiene, and avoid contact with sick people or animals. Stay updated on local health advisories and follow any restrictions imposed by authorities.
Key Takeaways
Nipah virus remains a serious health threat with a high death rate and no specific treatment currently available. The recent outbreak in West Bengal reminds us that this virus can strike anywhere, especially in regions where fruit bats are common.
Understanding how the virus spreads and knowing what symptoms to watch for can save lives. Simple prevention measures like washing hands, avoiding contaminated food, and staying away from sick people and animals can significantly reduce your risk.
While scientists work on developing vaccines and treatments, our best defense remains awareness and prevention. If you develop any symptoms after possible exposure, seek medical help immediately without delay.
Remember that staying informed about health threats is crucial for protecting yourself and your family. By following the guidelines shared in this article and staying updated on the latest health advisories, you can reduce your risk of infection and help prevent the spread of this dangerous virus in your community.
Want to Stay Updated on Important Health Topics? Visit Mensbuddy.com regularly for more helpful articles on health, wellness, and medical conditions that affect men and their families. Our easy-to-understand guides help you make informed decisions about your health.